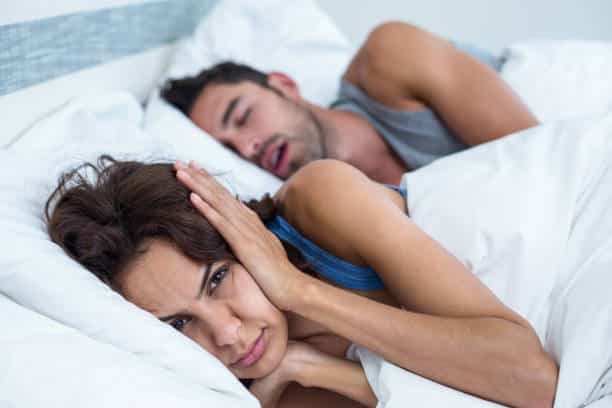
What is snoring
Snoring is the hoarse or harsh sound that occurs when air flows past relaxed tissues in your throat, causing the tissues to vibrate as you breathe. Almost everyone snores occasionally, and it occurs in around 40% of adult women and 57% of adult men. However, according to the British Snoring & Sleep Apnea Association, studies have found that men are twice as likely to be referred for a sleep study than women.
What causes snoring?
Snoring happens when air flows through your throat when you breathe in your sleep. This causes the relaxed tissues in your throat to vibrate, which leads to harsh, possibly irritating sounds.
Snoring may disrupt your sleep or that of your partner. Even if it’s not bothering you too much, snoring is not a symptom to ignore. In fact, snoring may indicate a serious health condition, such as:
- obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), or blocked airways
- obesity
- an issue with the structure of your mouth, nose, or throat
- sleep deprivation
In other cases, snoring may be caused simply by sleeping on your back or drinking alcohol too close to bedtime.
SUMMARY: Snoring can be caused by a number of factors, such as the anatomy of your mouth and sinuses, alcohol consumption, allergies, a cold, and your weight. When you doze off and progress from a light sleep to a deep sleep, the muscles in the roof of your mouth (soft palate), tongue and throat relax.
Sleep Apnea Snoring
Snoring is often associated with a sleep disorder called obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). Not all snorers have OSA, but if snoring is accompanied by any of the following symptoms, it may be an indication to see a doctor for further evaluation for OSA:
- Witnessed breathing pauses during sleep
- Excessive daytime sleepiness
- Difficulty concentrating
- Morning headaches
- Sore throat upon awakening
- Restless sleep
- Gasping or choking at night
- High blood pressure
- Chest pain at night
- Your snoring is so loud it’s disrupting your partner’s sleep
- In children, poor attention span, behavioral issues or poor performance in school
OSA is frequently distinguished by loud snoring that is followed by silence while breathing stops or almost ceases. This reduction or pause in breathing may eventually cause you to awaken, and you might do so with a loud gasp or snort.
Due to sleep disruption, you can have light sleep. Throughout the course of the night, this breathing rhythm may be repeated numerous times. At least five times each hour of sleep is often when breathing slows or stops for people with obstructive sleep apnea.
Snoring immediately after falling asleep
If you have OSA, you usually begin snoring heavily soon after falling asleep. The snoring often becomes very loud. Snoring is interrupted by a long silent period while your breathing stops. The silence is followed by a loud snort and gasp, as you attempt to breathe.
How to Stop Snoring
To stop snoring, you can try changing your sleeping position or using a nasal device. But some medical conditions, such as chronic allergies and sleep apnea, can cause snoring and require treatment.
15. Snoring Remedies
How to prevent snoring: Simple home remedies are frequently effective in treating cases of snoring brought on by benign factors, such as sleeping position. Altering one’s way of life can also assist treat snoring.
1. Sleep on your side
Your tongue may shift to the back of your throat when you are sleeping on your back, partially obstructing the passage of air. Sleeping on your side may be all you need to do to allow air to flow easily and reduce or stop your snoring.
2. Get enough sleep
As advised by the American Academy of Sleep Medicine and Sleep Research Society, make sure you receive the 7-9 hours of sleep each night that people require. Sleep deprivation may increase your risk of snoring. This is because it can cause your throat muscles to relax, making you more susceptible to airway obstruction.
Snoring can also increase your risk of sleep deprivation since it leads to interrupted sleep.
3. Raise the head of your bed
By keeping your airways open, raising the head of your bed a few inches may help stop snoring. To get a little more height, you can use items like pillows or bed risers.
4. Use nasal strips or a nasal dilator
Stick-on nasal strips can be applied to your nose’s bridge to assist widen the nasal airway. This can improve the efficiency of your breathing and lessen or stop snoring.
You could also try an external nasal dilator, which is a stiffened adhesive strip that’s applied on top of the nose across the nostrils. This can decrease airflow resistance, making it easier to breathe.
5. Limit or avoid alcohol before bed
Try not to consume alcohol for at least 3 hours leading up to your bedtime. Alcohol can relax the throat muscles, causing snoring.
Alcohol can also disrupt your sleep in other ways.
6. Avoid taking sedatives before bed
If you take sedatives, talk with your doctor to see what your options are. Stopping sedative use before bed may ease your snoring. Like alcohol, sedatives can also cause muscles such as your throat muscles to relax.
7. Try to stop smoking, if you smoke
Your snoring may get worse if you smoke regularly. Smoking may raise your risk of OSA or make the condition worse, which is one explanation for this. Talk with a doctor about therapies — such as gum or patches — that can help you quit.
8. Maintain a moderate weight
Losing weight will assist in reducing throat tissue if you are overweight. Your snoring can be brought on by too much tissue.
You can lose weight by reducing your overall caloric intake by eating smaller portions and more nutrient-rich foods. Try to get regular exercise daily. You may also consider reaching out to a doctor or a nutritionist for help.
Medical treatments for snoring
It’s crucial to consult a doctor if you snore in some circumstances so that you can receive the necessary medical therapy to address the underlying condition. Here are medical treatments commonly used to treat snoring and its various causes:
9. Treat chronic allergies
Allergies can reduce airflow through your nose, which forces you to breathe through your mouth. This increases the likelihood that you’ll snore.
Talk with a doctor about what kind of over-the-counter (OTC) or prescription allergy medications may improve your condition. They’re available in a variety of forms, such as nasal sprays, liquids, and pills.
Options include:
- nonsedating antihistamines, such as cetirizine (Zyrtec), levocetirizine (Xyzal), and loratadine (Claritin)
- sedating antihistamines, such as diphenhydramine (Benadryl)
- inhaled nasal corticosteroids, such as fluticasone (Flonase) and triamcinolone (Nasacort)
- oral decongestants, such as pseudoephedrine (Sudafed) and phenylephrine (Sudafed PE), for short-term use only
- leukotriene modifiers, such as montelukast (Singulair) and zileuton (Zyflo)
10. Correct anatomical structural problems in your nose
Some people are born with or experience an injury that gives them a deviated septum. This is the misalignment of the wall that separates both sides of the nose, which restricts airflow. A deviated septum may cause mouth breathing during sleep, resulting in snoring. It may be necessary to get surgery, called septoplasty, to correct this condition.
11. Use a continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) machine for OSA
The CPAP machine is the standard treatment for OSA. It requires you to wear a pressurized air mask over your nose, mouth, or both when you sleep. This can help keep your airways open. Different types of masks are available, including ones that are more comfortable for people with glasses or who breathe through their mouths during sleep.
12. Use an oral appliance
Oral appliances are customized devices prescribed and fitted by dentists. These devices increase the size of the upper airway during sleep, which decreases snoring.
They typically work by one or more of the following mechanisms:
- advancing the lower jaw (mandible)
- changing the position of the soft palate
- retracting the tongue
The American Academy of Sleep Medicine and the American Academy of Dental Sleep Medicine recommend oral appliances for people who request treatment for their snoring and have not found relief with conservative measures.
13. Wear palatal implants
Also called the pillar procedure, this surgery is designed to reduce or stop snoring and improve OSA. To lessen tissue vibration during this treatment, small implants are placed in the soft palate. To assist you stop snoring, palatal implants are made to strengthen your soft palate.
This treatment is appropriate for people with mild to moderate sleep apnea. It’s not recommended for people who have severe sleep apnea or are overweight.
14. Get uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UPPP)
UPPP is a procedure used to remove excess tissue in your throat to widen the airway. This can sometimes allow air to move through the throat more easily when you breathe, reducing snoring. It can be done through traditional surgical techniques or laser-assisted, which allows for outpatient therapy.
15. Consider radiofrequency ablation (RFA)
This minimally invasive treatment uses low intensity radio waves to shrink the tissue on your soft palate. RFA is sometimes referred to as Somnoplasty, which is the name of a trademarked version of the procedure.
When to see a doctor
You’re not the only one that snores. The American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery Foundation estimates that almost half of Americans snore.
Both your partner’s and your own sleep may be disturbed by snoring. It may be a sign of a dangerous medical problem in addition to being bothersome. You can better control your sleep by speaking with a doctor and attempting one or more of the aforementioned therapy choices.
Reach out to a doctor if:
- You have signs or symptoms of sleep apnea, such as:
- gasping for air while you sleep
- nocturia, or frequent urination at night
- hypersomnia, or excessive daytime sleepiness
- waking up with a dry mouth or sore throat
- waking up with a headache
- Snoring affects the quality of your sleep.
- Home remedies and lifestyle changes do not reduce your snoring.
FAQ
What causes snoring in females?
Weight gain is one of the reasons for snoring loud. Hormonal imbalance, pregnancy, and menopause are the transitional phases in which there is an alteration in a women’s metabolism. Snoring and weight gain are closely associated. Excessive weight leads to skin build up around the neck area.
Is snoring bad?
Loud or long-term snoring increases the risk of heart attack, stroke and other health problems. You may be able to stop snoring by losing weight and avoiding alcohol before bed. If snoring keeps you awake or disrupts your partner’s sleep, talk to your provider about treatments.
How do I stop snoring?
The tendency to snore could be more due to head position than body position, with people snoring less when their heads are turned to the side. If you know that you’re snoring at night and you generally sleep on your back, try to fall asleep on your side instead.
how to stop snoring naturally:
- If you’re overweight, lose weight.
- Sleep on your side
- Raise the head of your bed
- Nasal strips or an external nasal dilator
- Treat nasal congestion or obstruction
- Limit or avoid alcohol and sedatives
- Quit smoking
- Get enough sleep.
What does snoring mean?
Snoring is the hoarse or harsh sound that occurs when air flows past relaxed tissues in your throat, causing the tissues to vibrate as you breathe. Nearly everyone snores now and then, but for some people it can be a chronic problem. Sometimes it may also indicate a serious health condition. In addition, snoring can be a nuisance to your partner.
Is snoring dangerous?
Occasional snoring due to a cold or flu is usually harmless. But very loud or frequent snoring can be a sign of sleep apnea, which is a serious disorder. Long-term snoring increases the risk of health problems, including: Decreased blood oxygen levels.
What type of snoring is dangerous?
Throat based snoring is the loudest type of snoring you will hear and it’s usually also the most dangerous. Throat snoring is usually a strong indicator of sleep apnea. When you have sleep apnea, you stop breathing at night due to an obstruction in your airway.
Share: